A few weeks ago, we considered a hypothetical conversation between you and your CEO:
"How can we leverage generative AI for our business?"
"Let's make a ChatGPT for our users. They can ask questions about our knowledge base and get back informative answers.”
"...How do we do that?"
And in answering that last question, we looked at three ways to build a chat interface on top of your company documents. Here's the original post if you're interested.
But I wanted to take another stab at the first question: "How can we leverage generative AI for our business?"
With so much hype around generative AI, there's a big gap between perceived impacts and actual implementations. What types of generative models make sense for us? Where can we apply products or techniques to our existing business?
So let’s look at what’s actually possible today with generative AI, and then we’ll see how to apply those possibilities for three common company functions: sales, marketing, and customer service.
What's possible
ChatGPT regularly steals the spotlight, but there's much more to generative AI than new and improved chatbots. I've pulled some of the most common use cases, but this is far from a comprehensive list.
Many industries will create models for their niche, like drug discovery or music video generation. But most individual companies won't be in the business of designing and training bespoke models from scratch.
That being said, this post mostly focuses on the what, not the how. Applying generative AI to your business can take various forms. It could mean fine-tuning models, using hosted APIs, or paying for SaaS products with AI features. Many of these techniques are currently available as SaaS product features!
But whether you're building it or buying it, getting value from generative AI doesn’t require advanced machine learning skills.
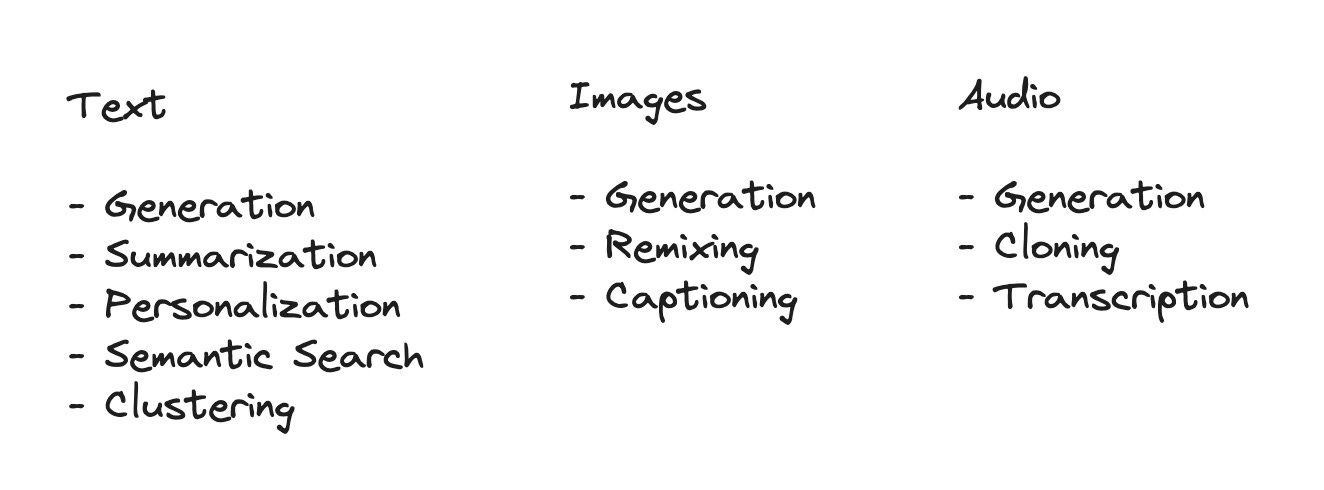
Text
Generation: Besides chatting, generative AI can create tailored text for almost any application. That could mean emails, articles, or code snippets. It could mean text translation or document analysis. With ChatGPT, it means developing strategy or thinking through problems. Right now, the instruction-tuned chatbots are king, but fine-tuning models will open up many more use cases in the long run.
Summarization: There's far too much to read today, and AI summaries can be a huge time saver. Each org has different processes, but summarization can be helpful wherever professionals need to digest a lot of information quickly. Think managers reviewing documents or researchers analyzing papers.
Personalization: Generative AI can create personalized user content, like emails, ads, or recommendations. We're not there yet, but eventually, we'll be able to create fully-personalized media as well. This can help businesses increase engagement, boost conversions, and improve customer satisfaction.
Semantic Search: Traditional search relies on matching keywords, but modern language models can understand the meaning of a query and find relevant information even without an exact word match. This makes surfacing relevant messages or documents significantly easier, whether in Slack channels, Jira tickets, or public knowledge bases.
Classification/Clustering: AI can categorize and group documents based on their content, which helps organize large amounts of unstructured data, like customer feedback or academic research. Classification and clustering are two separate techniques, but for our purposes, we'll think of them both as "bucketing."
Image/Video
Generation: AI can now generate realistic images from descriptions, which can be used to create digital art, design products, or visualize concepts in marketing and advertising. The earliest tools focused on general prompting, but new products focus on specific styles or asset types (i.e. game dev, HTML/CSS, etc.). Video generation is also possible, though we're still in the early stages.
Remixing: Given an existing image, AI can modify it according to specific instructions, like changing the color of a shirt or adding a sunset to the background. Or, it can be blended with a second image to create things like custom QR codes.
Captioning: AI can analyze an image and generate a descriptive caption, which can be used for making content more accessible, helping visually impaired users, or indexing images for search.
Audio
Generation: We've come a long way with AI-generated speech. The best-in-class AI voices are nearly indistinguishable from real people. That means we can create voiceovers at scale for videos, messages or music.
Cloning: Given a sample of someone's voice, AI can generate new speech as that person. That means personalizing voice clips or dubbing videos. Of course, there are plenty of ethical considerations around voice cloning, and most platforms will only clone a voice with that person's explicit consent.
Transcription: A key feature of working with audio is transcription. AI tools have made transcription incredibly cheap, making it much easier to work with audio clips in new ways. Audio clips can be quickly analyzed or summarized, or they can be translated into different languages.
Applied AI
Now that we've seen these concepts at a high level, let's take a look at some ideas for implementation. We’ll cover three of the most common company functions: customer service, sales, and marketing.
Customer service
Answering support tickets is not something most employees jump out of bed to work on. But because it's often measured through the lens of ruthless efficiency, experimenting with AI is something that many organizations are keen to do.
The obvious use case is… a better chatbot. Combining semantic search with summarization allows us to build a chatbot on top of the company's knowledge base for faster (and, more importantly, automated) answers. But we can keep going: text generation means we can pre-write ticket responses. We're used to dealing with templates and macros, but we can attempt to tailor the response even further while still saving time.
We can also summarize an existing ticket thread for a support agent. We've all experienced having a support ticket handed off or escalated, only to have the new person lose the entire context of our problem. So we explain the issue - again. Why not auto-generate summaries of support calls or tickets whenever a new agent takes over?
Over time, with enough data, we can use clustering to pull out the most common questions or issues that customers have. Rather than making simple word clouds or relying on brittle tagging systems, we can group issues into semantic buckets for topics like "where is my order" or "how do I cancel."
Sales
With sales, the name of the game is personalization. Sales departments have been focused on tailoring their approach for years, and generative AI takes that to the next level. AI advancements have been a boon for data enrichment companies: ChatGPT can scrape and parse websites for leads with a few clicks, and classification makes it easy to structure company data.
And, of course, there's sales email copy. Generation works great for this, as indicated by the tidal wave of AI sales email startups. Customizing the tone, the ask, and adding a personalized touch are straightforward with the right prompt. And you can add in your CRM data to mention the recent LinkedIn post they made or the fact that they're celebrating X years in their role. Like customer service, templates are commonplace, but AI can help solve the blank canvas problem when writing new ones.
Combining all of these things, we can layer on audio and video generation to create fully tailored video messages. It's possible to remix a pre-recorded template to include company names and descriptions in an outbound sales video. Asynchronous messages are great for generated audio - most models are slow right now, making real-time conversations clunky.
There's AI for during and after the sales call, too. Meetings can be summarized and analyzed for common customer concerns, or reviewed for specific insights. Over time, the most common scenarios can be added to a sales playbook.
Marketing
Marketers can leverage text generation for a wide variety of use cases. With language models, we can brainstorm ideas for content marketing posts and then write the articles themselves (paired with a human for fact checking). Given a full-length article, AI can turn it into a series of smaller chunks for Twitter or Threads. Or, given a full-length podcast episode, we can use AI to create clips and audiograms for TikTok, YouTube Shorts, or Instagram Reels.
If you have an established history of blog posts or Tweets, perhaps analyze your best ones and use AI to remix them for evergreen content. Or, consider translating your back catalog of articles into multiple languages. If you want to optimize your product pages for SEO, language models can handle that. And if you want to enrich your posts with high-quality images (and you don't have a stock photo subscription), use image generation to create the perfect splash image.
Like sales, marketing can also leverage personalized copy. Getting your brand voice correct is the hardest part, but with the right prompt, it's possible. And you can layer in personalized data like a customer's sales history or a unique discount code. Working with ChatGPT can also help you brainstorm promotion ideas for your audience.
Final thoughts
If it wasn’t obvious, I’ve barely scratched the surface here. The implementation ideas I’ve listed make the most sense for white-collar B2B companies - far from the only type of organization. Hopefully, it’s still a useful window into what we can do beyond “ChatGPT for X.”
It’s also worth mentioning that there are plenty of caveats to using these tools: ChatGPT will lie to you, Midjourney’s copyright status is a legal gray area, and so on. But the tools will improve over time, and we’ll figure out how to incorporate them more broadly. Taking advantage of these technologies today will put you ahead of the curve.
And I’d also like to leave you with a thought on generation and personalization. We can now do things at scale that weren’t previously possible, and with great new power comes new responsibility. From a previous post:
AI shouldn't replace the thoughtfulness and intention that goes into designing [user] experiences. The best experiences [businesses] can create are ones that are delightfully authentic. Without that authenticity, AI-generated content just becomes spam.







I like this a lot: "Taking advantage of these technologies today will put you ahead of the curve."
Folks don't really understand what's happening, and how many folks are just going to be left in the dust.